It's hard for me to sort out my feelings - a phrase that each of us has come across: in books , in movies , in life ( someone's or our own). But it is very important to be able to understand your feelings.
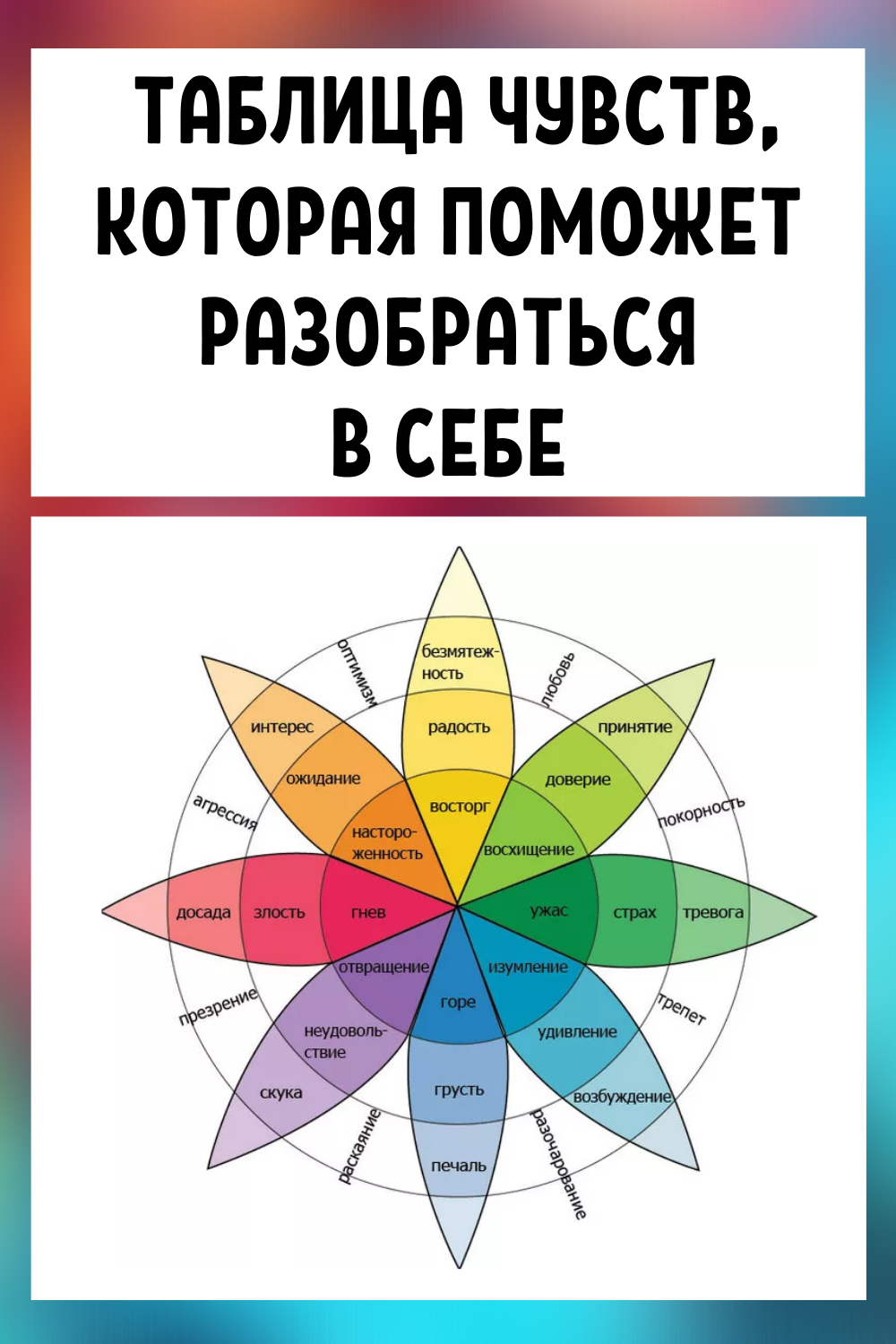
Wheel of Emotions by Robert Plutchik
Some believe - and perhaps they are right - that the meaning of life is in feelings. And in fact , , , remain with us . And the measure of what is happening can also be our experiences: the richer , more diverse , brighter they , the more fully we feel life.
What are feelings? The simplest definition: feelings are what we feel. This is our attitude to certain things ( objects). There is also a more scientific definition: feelings ( higher emotions) are special mental states that are manifested by socially conditioned experiences that express a person’s long-term and stable emotional relationship to things.
How are feelings different from emotions?
Sensations are our experiences that we experience through the senses , and we have five of them. Sensations are visual , auditory , tactile , gustatory and odor sensations ( our sense of smell).
Everything is simple with sensations: stimulus - receptor - sensation. Our consciousness interferes with emotions and feelings - our thoughts , attitudes , our thinking. Emotions are influenced by our thoughts. Conversely, emotions affect our thoughts. We will discuss these relationships in more detail a little later. But now let's remember once again one of the criteria for psychological health , namely point 10: we are responsible for our feelings , it depends on us what they will be.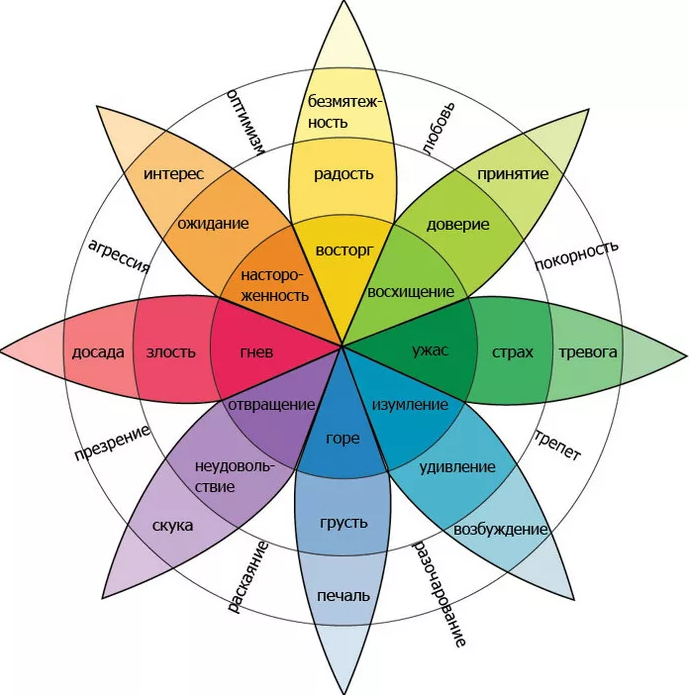 It is important.
It is important.
Fundamental emotions
All human emotions can be distinguished by the quality of experience. This aspect of a person's emotional life is most clearly presented in the theory of differential emotions by the American psychologist K. Izard. He identified ten qualitatively different "fundamental" emotions: interest-excitement , joy , surprise , grief-suffering , , disgust-disgust , contempt -neglect , fear-horror , shame-shyness , guilt-repentance . K. Izard classifies the first three emotions as positive , the remaining seven as negative. Each of the fundamental emotions underlies a whole spectrum of states that differ in severity. For example , within the framework of such a single-modal emotion as joy, one can single out joy-satisfaction , joy-delight , joy-jubilation , joy-ecstasy and others. From the combination of fundamental emotions, all other , more complex , complex emotional states arise. For example , anxiety can combine fear , anger , guilt, and interest.
1. Interest is a positive emotional state that contributes to the development of skills and abilities , the acquisition of knowledge. Interest-excitation is a feeling of capture , curiosity.
2. Joy is a positive emotion associated with the ability to sufficiently fully satisfy an urgent need , the probability of which before that was small or uncertain. Joy is accompanied by self-satisfaction and satisfaction with the surrounding world. Obstacles to self-realization are also obstacles to the emergence of joy.
3. Surprise - an emotional reaction that does not have a clearly expressed positive or negative sign to sudden circumstances. Surprise slows down all previous emotions , directing attention to a new object and can turn into interest.
4. Suffering ( grief) - the most common negative emotional state associated with obtaining reliable ( or seeming such) information about the impossibility of satisfying the most important needs , the achievement of which before that seemed more or less likely. Suffering has the character of asthenic emotion and more often occurs in the form of emotional stress. The most severe form of suffering is grief associated with irretrievable loss.
5. Anger - a strong negative emotional state , occurring more often in the form of affect; arises in response to an obstacle in achieving passionately desired goals. Anger has the character of a sthenic emotion.
6. Disgust - a negative emotional state caused by objects ( objects , people , , contact with which ( physical or communicative) comes into sharp conflict with the aesthetic , moral or ideological principles and attitudes of the subject. Disgust , if combined with anger , can interpersonally motivate aggressive behavior. Disgust , like anger , can be self-directed , lowering self-esteem and causing self-judgment.
7. Contempt - a negative emotional state that occurs in interpersonal relationships and is generated by a mismatch of life positions , views and behavior of the subject with those of the object of feeling. The latter are presented to the subject as base , not corresponding to accepted moral standards and ethical criteria. A person is hostile to those whom he despises.
8. Fear - a negative emotional state that appears when the subject receives information about the possible damage to his well-being , about real or imagined danger. In contrast to the suffering caused by direct blocking of the most important needs , a person experiencing the emotion of fear has only a probabilistic forecast of possible trouble and acts on the basis of this forecast ( often insufficiently reliable or exaggerated). The emotion of fear can be both sthenic and asthenic in nature and proceed either in the form of stressful conditions , or in the form of a stable mood of depression and anxiety , or in the form of affect ( horror).
9. Shame - a negative emotional state , expressed in the awareness of the inconsistency of one's own thoughts , actions and appearance, not only with the expectations of others , but also with one's own ideas about appropriate behavior and appearance.
10. Guilt - a negative emotional state , expressed in the realization of the unseemliness of one's own act , thought or feelings and expressed in regret and repentance.
Table of human feelings and emotions
And I also want to show you a collection of feelings , emotions , states that a person experiences during his life - a generalized table that does not pretend to be scientific , but will help you better understand yourself.
The table is taken from the site "Communities of dependent and co-dependent", the author is Mikhail. All human feelings and emotions can be divided into four types. It is fear , anger , sadness and joy. To what type this or that feeling belongs can be found from the table.
And for those who read the article to the end. The purpose of this article is to help understand your feelings , in what they are. Our feelings largely depend on our thoughts. Irrational thinking often underlies negative emotions. By correcting these mistakes ( working on thinking), we can be happier and achieve more in life. There is an interesting , but persistent and painstaking work on oneself. You are ready?
Save so you don't lose